
- #Free fall and acceleration due to gravity lab series#
- #Free fall and acceleration due to gravity lab free#
We know, experimentally, that a body undergoing a free.
#Free fall and acceleration due to gravity lab free#
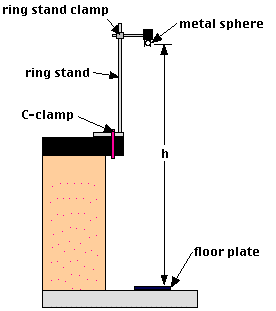
This provides a way of estimating air resistance by studying the differences in the two different values. THEORY: A body falling under the influence of gravity only is said to be in a state of a free fall. On the way up, gravity and air resistance are working in the same direction, and on the way down, gravity and air resistance are working in opposite directions. This can lead to an interesting physics lesson in itself. Note the business about fitting the two different halves of the toss. So you need to keep well up into your parabola when selecting your range. Attach the right angle clamp to a vertical support rod. Keep in mind when selecting a portion of your graph to analyze that the program looks at a few data points on either side of the range you select. Experiment P007: Acceleration due to Gravity (Free Fall Adapter) 1. The racquetball has less air resistance, so it gives slightly higher numbers. Using a quadratic fit, we analyzed the entire parabola, the first half of the parabola, and the second half of the parabola. We tossed a racquetball and then a basketball using the Motion Detector.

We performed this experiment with a Motion Detector to see what values we would obtain.

#Free fall and acceleration due to gravity lab series#
Mostly this results in noisy time series for freefall accelerations. Tiny errors in distance measurements cause fairly large errors in acceleration measurements. The distance resolution of the Motion Detector is about 3 mm.This timing error is minor for objects undergoing small accelerations, but in freefall the acceleration is large. Tiny errors in time measurements cause large errors in acceleration measurements. We know the exact time at which the sound is produced, but x varies with the distance measured. This occurs a time, x, after the ultra sound is produced. The value of acceleration due to gravity, g, can be found by dropping a steel ball bearing and measuring the time it takes to fall, however the the very. The exact time of measurement is the instant when the ultrasound bounces off the object. The exact time of the measurement is not controlled.There are a few factors that make the Motion Detector less-than-perfect for this type of measurement: If that is your goal, we recommend using a Photogate and a Picket Fence. Motion Detectors do not provide the best measurement of the acceleration due to gravity.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
